Ten days have passed since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared a global health emergency because of the novel coronavirus or 2019-nCoV. Up to this day, the situation remains dire with 37,499 confirmed cases (majority in China), 813 deaths, and 25 countries affected by the rapidly spreading virus.
At the same time, news about 2019-nCoV continues to spread, including unverified information that do more harm than good, and causing unnecessary panic among communities around the world. To make matters worse, some have even expressed anti-Chinese sentiment, since the virus is reported to have originated from Wuhan in the province of Hubei, China.
WHO Dispels Myths About Novel Coronavirus
To set things straight and dispel some misconceptions that have been going around, the WHO has issued a “myth busters” guide, containing public advice about 2019-nCoV. Based on this guide, we present the following questions and answers regarding the much-feared virus:
#1 – Does 2019-nCoV affect a certain age group only?
NO. The novel coronavirus affects people of ALL ages. Nonetheless, older people, as well as those with preexisting conditions (e.g. heart disease, diabetes, asthma) appear to more susceptible to the disease. In any case, people of all ages are advised to protect themselves by following good hygiene and staying fit as much as possible.
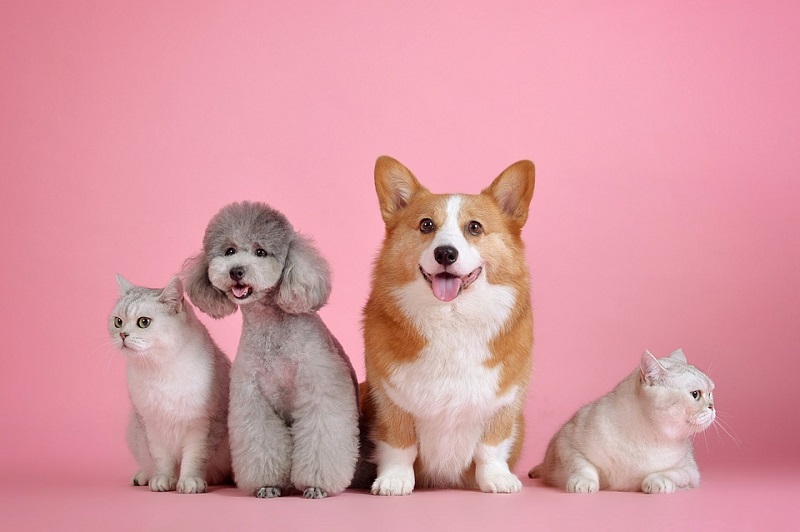
#2 – Can my pets at home spread 2019-nCoV?
There is NO evidence to suggest that domesticated animals like cats and dogs can be infected by 2019-nCoV. Still, it is always a good idea to wash your hands after interacting with animals and pets, to protect yourself from bacteria like Salmonella and E.coli.
#3 – Is it safe to receive a letter or package that came from China?
YES. Previous analysis have shown that coronaviruses do not survive long on things like letters or packages. So you are not at risk of contracting 2019-nCoV if you receive a package from China.
#4 – Can applying sesame oil block 2019-nCoV from entering the body?
NO. Sesame oil has not been proven to block or kill 2019-nCoV. Certain chemical disinfectants — including bleach, chloroform, and 75% ethanol — have been observed to kill the virus on surfaces. However, they have little effect when applied on the skin or under the nose. These may also be too dangerous to apply on your skin!
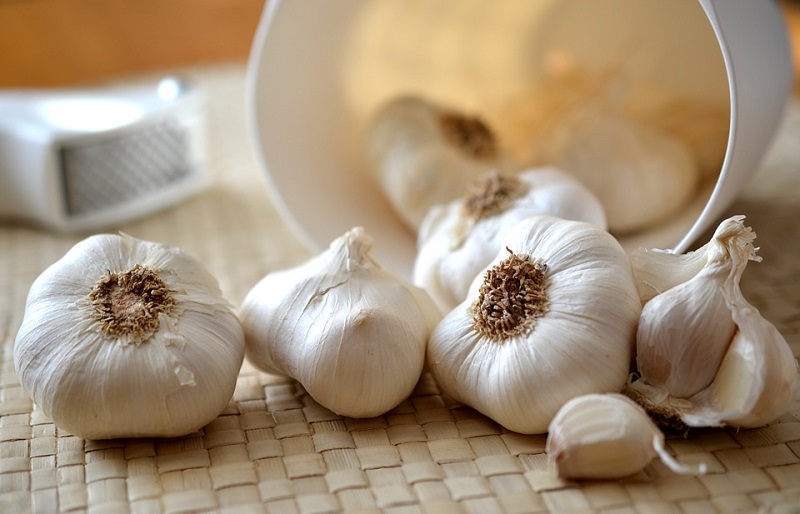
#5 – Can eating garlic protect a person from 2019-nCoV?
There is NO evidence to suggest that eating garlic has protected people from being infected with 2019-nCoV. Nevertheless, garlic is still considered as a healthy food that may contain antimicrobial properties.
#6 – Can rinsing the nose with saline protect a person from 2019-nCoV?
There is NO evidence to suggest that rinsing the nose with saline can protect a person from 2019-nCoV. Some limited evidence suggest that regularly rinsing the nose with saline can help a person recover faster from the common cold, but this has not been proven to prevent respiratory infections.
#7 – Can gargling with mouthwash protect a person from 2019-nCoV?
There is NO evidence to suggest that garling with mouthwash can protect a person from 2019-nCoV. Certain brands have been observed to kill certain microbes in the saliva for a few minutes, but this does not indicate that they can help protect against 2019-nCoV.
#8 – Can vaccines against pneumonia protect a person from 2019-nCoV?
NO. Anti-pneumonia vaccines do not provide protection against 2019-nCoV, although vaccination against respiratory illnesses is generally highly recommended. At this time, researchers are still trying to develop a vaccine against 2019-nCoV.
#9 – Can antibiotics treat and prevent 2019-nCoV?
NO. Antibiotics can work against bacteria only, and not viruses such as 2019-nCoV. Antibiotics should not be used a a means of treatment or prevention against the new virus. Nonetheless, if you become hospitalized due to 2019-nCoV, you may receive antibiotics, for the reason that bacterial co-infection is possible.
#10 – Is there a specific medicine to treat or prevent 2019-nCoV?
As of this writing, there is NO specific medicine to treat or prevent 2019-nCoV. But for those who have been infected, appropriate care should be given to relieve and treat symptoms. Furthermore, those with severe illnesses should receive the best possible supportive care.
As the virus continues to spread, it is vital for everyone to be updated about the latest news, including preventive measures and possible treatments. More importantly, we should remain calm and rely only on trusted information sources. Speaking of which, here are some tips for protecting yourself against the novel coronavirus, issued by the Department of Health (DOH).
DISCLAIMER: The details above are presented for information-sharing purposes only. To know more about the latest news and advisories on the novel coronavirus or 2019-nCoV, please visit the official website of the World Health Organization (WHO).